[고2] 2024년 10월 – 35번: 공공 자원의 과잉 사용으로 인한 '공유지의 비극' 설명
Any new resource (e.g., a new airport, a new mall) always opens with people benefiting individually by sharing a common resource (e.g., the city or state budget). Soon, at some point, the amount of traffic grows too large for the "commons" to support. Traffic jams, overcrowding, and overuse lessen the benefits of the common resource for everyone ─ the tragedy of the commons! If the new resource cannot be expanded or provided with additional space, it becomes a problem, and you cannot solve the problem on your own, in isolation from your fellow drivers or walkers or competing users. The total activity on this new resource keeps increasing, and so does individual activity; but if the dynamic of common use and overuse continues too long, both begin to fall after a peak, leading to a crash. What makes the "tragedy of commons" tragic is the crash dynamic ─ the destruction or degeneration of the common resource's ability to regenerate itself.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭)


원문 텍스트 및 OCR
 |
Archetype 4. Tragedy of the Commons Management Principle: Continuous Increase in Use of a Common Resource Will Eventually Overstrain the Resource Until It Crashes Any new resource (e.g., a new expressway, a new airport, a new mall, a new charter school, a children's park, a new credit union) always opens with people benefiting individually by sharing a common resource (e.g., the city or state budget). Soon, at some point, the amount of traffic grows too large for the “commons” to support; congestion, overcrowding, and overuse lessen the benefits of the common resource for everyone ~ the tragedy of the commons! If the new resource cannot be expanded or replenished with additional space, it becomes a constraint, a problem, and you cannot solve the problem on your own, in isolation from your fellow drivers or pedestrians or competing users. The total activity on this new resource keeps increasing, and so does individual activity; but both begin to fall after a peak, the latter faster than the former. Eventually, if the dynamic of common use and overuse continues too long, the total activity will also hit a peak and crash. What makes the “tragedy of commons” tragic is the crash dynamic - the destruction or degeneration of the common resource's ability to regenerate itself. The tragedy of the commons, thus, is a corollary of the “limits to growth” archetype. |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

[고2] 2024년 10월 – 36번: 뇌가 시각 정보를 단순화하고 일반화하는 방식으로 에너지를 절약
Theoretically, our brain would have the capacity to store all experiences throughout life, reaching the quality of a DVD. However, this theoretical capacity is offset by the energy demand associated with the process of storing and retrieving information in memory. As a result, the brain develops efficient strategies, becoming dependent on shortcuts. When we observe a face, the visual image captured by the eyes is highly variable, depending on the point of view, lighting conditions and other contextual factors. Nevertheless, we are able to recognize the face as the same, maintaining the underlying identity. The brain, rather than focusing on the details of visualization, creates and stores general patterns that allow for consistent recognition across diverse circumstances. This ability to match what we see with general visual memory patterns serves as an effective mechanism for optimizing brain performance and saving energy. The brain, being naturally against unnecessary effort, constantly seeks to simplify and generalize information to facilitate the cognitive process.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭) - 구글 검색 불가

원문 텍스트 및 OCR
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)
[고2] 2024년 10월 – 37번: 과학 연구에서 창의적 해석이 이론 형성에 미치는 영향
Where scientific research is concerned, explanatory tales are expected to adhere closely to experimental data and to illuminate the regular and predictable features of experience. However, this paradigm sometimes conceals the fact that theories are deeply loaded with creative elements that shape the construction of research projects and the interpretations of evidence. Scientific explanations do not just relate a chronology of facts. They construct frameworks for systematically chosen data in order to provide a consistent and meaningful explanation of what is observed. Such constructions lead us to imagine specific kinds of subject matter in particular sorts of relations, and the storylines they inspire will prove more effective for analyzing some features of experience over others. When we neglect the creative contributions of such scientific imagination and treat models and interpretive explanations as straightforward facts ─ even worse, as facts including all of reality ─ we can blind ourselves to the limitations of a given model and fail to note its potential for misunderstanding a situation to which it ill applies.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭)


원문 텍스트 및 OCR
 |
Mechanistic Stories in Humane Practices Where scientific research is concerned, explanatory tales are expected to adhere closely to experimental data and to illuminate the regular and predictable features of experience. However, and as Misak has explained, this mode of operation sometimes disguises the fact that theories are deeply laden with creative elements that shape the construction of research projects and the interpretations of evidence. Scientific explanations do not just relate a chronology of facts. They construct frameworks for—they “emplot”—systematically chosen data in order to provide a coherent and meaningful explanation of what is observed. Such constructions lead us to imagine specific kinds of subject matter in particular sorts of relations, and the storylines they inspire will prove more effective for analyzing some features of experience over others. When we neglect the creative contributions of the scientific imagination and treat models and interpretive explanations as straightforward facts—even worse, as facts exhaustive of reality—we can blind ourselves to the limitations of a given model and fail to note its potential for misunderstanding a situation to which it ill applies. |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

[고2] 2024년 10월 – 38번: 문학이 사회적 변화를 촉진하거나 방해할 수 있는 방식
We encounter contrary claims about the relation of literature to action. Theorists have maintained that literature encourages solitary reading and reflection as the way to engage with the world and thus counters the social and political activities that might produce social change. At best it encourages detachment or appreciation of complexity, and at worst passivity and acceptance of what is. But on the other hand, literature has historically been seen as dangerous: it promotes the questioning of authority and social arrangements. Plato banned poets from his ideal republic because they could only do harm, and novels have long been credited with making people dissatisfied with their lives and eager for something new. By promoting identification across divisions of class, gender, and race, books may promote a fellowship that discourages struggle; but they may also produce a keen sense of injustice that makes progressive struggles possible. Historically, works of literature are credited with producing change: Uncle Tom's Cabin, a best-seller in its day, helped create a revulsion against slavery that made possible the American Civil War.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭)


원문 텍스트 및 OCR
 |
We also encounter contrary claims about the relation of literature to action. Theorists have maintained that literature encourages solitary reading and reflection as the way to engage with the world and thus counters the social and political activities that might produce change. At best, it encourages detachment or appreciation of complexity, and at worst passivity and acceptance of what is. But, on the other hand, literature has historically been seen as dangerous: it promotes the questioning of authority and social arrangements. Plato banned poets from his ideal republic because they could only do harm, and novels have long been credited with making people dissatisfied with the lives they inherit and eager for something new—whether life in big cities or romance or revolution. By promoting identification across divisions of class, gender, race, nation, and age, books promote a ‘fellow-feeling’ that may discourage struggle but may also produce identifications and a keen sense of injustice that make progressive struggles possible. Historically, works of literature are credited with producing change: Harriet Beecher Stowe’s *Uncle Tom’s Cabin*, a bestseller in its day, helped create a revulsion against slavery that made possible the American Civil War. |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

[고2] 2024년 10월 – 39번: Hobbes의 자연 상태에서 인간의 본성과 도덕적 자유의 한계
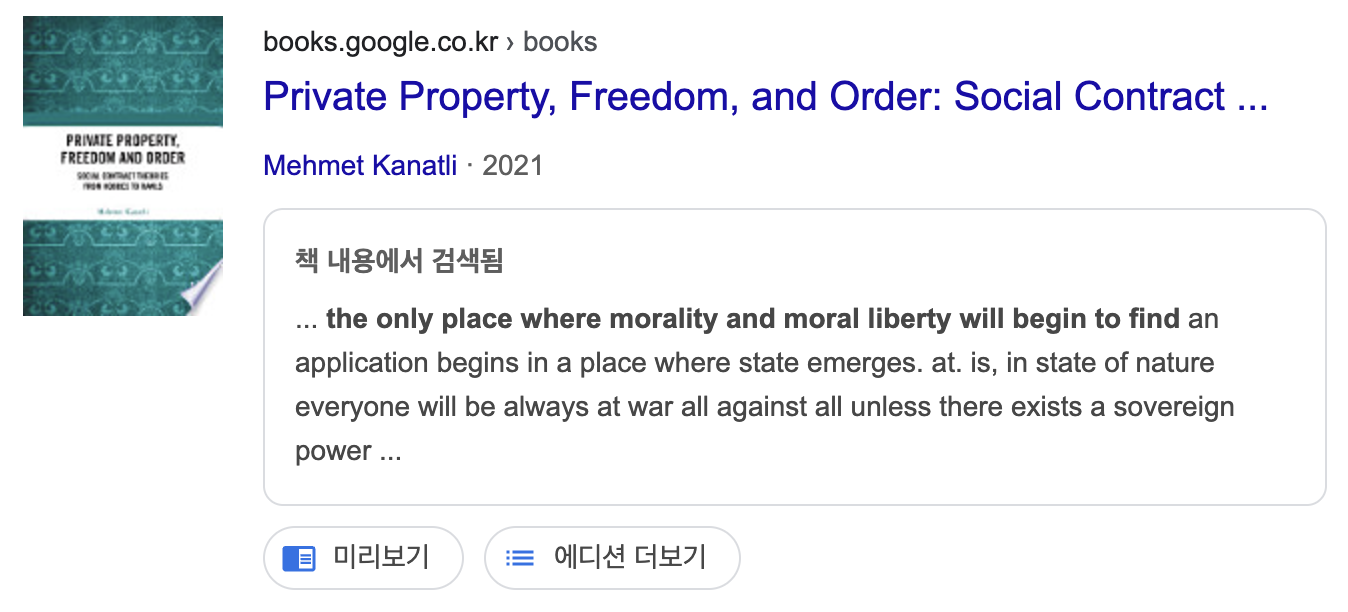
According to Hobbes, man is not a being who can act morally in spite of his instinct to protect his existence in the state of nature. Hence, the only place where morality and moral liberty will begin to find an application begins in a place where a sovereign power, namely the state, emerges. Hobbes thus describes the state of nature as a circumstance in which man's life is "solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short". It means when people live without a general power to control them all, they are indeed in a state of war. In other words, Hobbes, who accepted that human beings are not social and political beings in the state of nature, believes that without the power human beings in the state of nature are "antisocial and rational based on their selfishness". Moreover, since society is not a natural phenomenon and there is no natural force bringing people together, what will bring them together as a society is not mutual affection according to Hobbes. It is, rather, mutual fear of men's present and future that assembles them, since the cause of fear is a common drive among people in the state of nature.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭)

원문 텍스트 및 OCR
 |
By continuing the same logic, Hobbes claims that the equality and freedom of people in terms of obtaining anything on nature leads to the enmity among individuals, for “if any two men desire the same thing, which nevertheless they cannot both enjoy, they become enemies; and in the way to their end (which is principally their own conservation, and sometimes their delectation only) endeavour to destroy or subdue one another” (Ibid). The important point that can be drawn from this Hobbesian description of the emergence of enmity among individuals in state of nature is the reality of scarce resources in nature which highly possibly lead to the enmity. In such a state of nature, for Hobbes, three principles lead to the state of war which are: “First competition; secondly, diffidence; thirdly, glory” (Ibid: 77). So, according to Hobbes, if there is no sovereign power over people, morality and so moral freedom will not be in question. Man is not a man who can act morally in spite of his instinct to protect his existence in such a state of nature. Hence, the only place where morality and moral liberty will begin to find an application begins in a place where state emerges. That is, in state of nature everyone will be always at war all against all unless there exists a sovereign power, namely state. Hobbes thus describes the state of nature as a circumstance in which man’s life is “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish and short” (Ibid: 78). In other words, when people live without a general power to fear them all, they are indeed in a state of war, and this war is the war of all against all (Ibid: 94). Hobbes, who accepted that human being is not social and political being in the state of nature (not zoon politikon in Aristotelian sense) (Ibid: 22), believes that human being in state of nature is an “antisocial and rational based on selfishness”. Moreover, since society is not a natural phenomenon and there is no natural force bringing people together, what will bring them together as a society is not mutual affection according to Hobbes. Rather, it is mutual fear of man’s present and future that brings them together, since the cause of fear is a common drive among people in the state of nature (Ibid: 24-25). |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

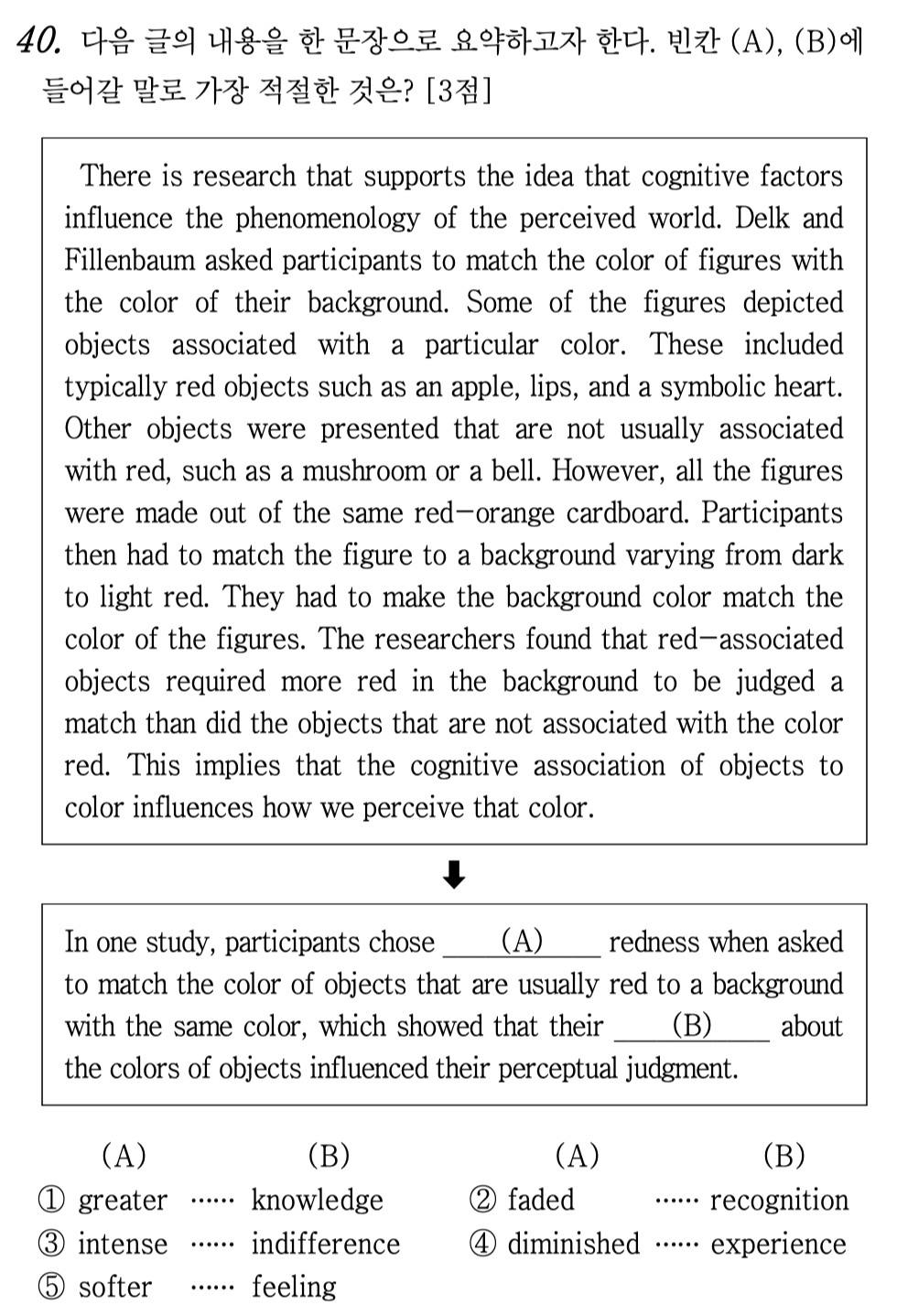
[고2] 2024년 10월 – 40번: 인지적 요소가 색 인식에 미치는 영향에 대한 연구
There is research that supports the idea that cognitive factors influence the phenomenology of the perceived world. Delk and Fillenbaum asked participants to match the color of figures with the color of their background. Some of the figures depicted objects associated with a particular color. These included typically red objects such as an apple, lips, and a symbolic heart. Other objects were presented that are not usually associated with red, such as a mushroom or a bell. However, all the figures were made out of the same red-orange cardboard. Participants then had to match the figure to a background varying from dark to light red. They had to make the background color match the color of the figures. The researchers found that red-associated objects required more red in the background to be judged a match than did the objects that are not associated with the color red. This implies that the cognitive association of objects to color influences how we perceive that color.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭) - 구글 검색 가능하지만 텍스트에 접근 불가능

원문 텍스트 및 OCR
  |
The view that cognitive and emotional factors influence the phenomenology of perception is known as cognitive penetration (Marchi & Newen, 2015). Cognitive penetration means that nonperceptual factors affect what we see, hear, taste, and feel. The opposing view is that perception is not affected by cognitive factors and that only our reporting of perception is. This view is called cognitive impenetrability (Firestone & Scholl, 2016). Impenetrability implies that our perception remains the same, regardless of our cognitive and emotional state. What changes instead is attention, expectation, or our mood state, which is different than our perceptual state. The dominant view in the field is that perception is cognitive impenetrable. However, recent research supports some instances in which cognitive or emotional factors influence the phenomenology of the perceived world. Delk and Fillenbaum (1965) asked participants to match the color of figures with the color of their background. Some of the figures depicted objects associated with a particular color. These included typically red objects such as an apple, lips, and a symbolic heart. Other objects were presented that are not typically associated with red, such as a mushroom or a bell. However, all the figures were made out of the same red-orange cardboard. Participants then had to match the figure to a background varying from dark to light red. They had to make the background color the same as the color of the figures. Delk and Fillenbaum found that red-associated objects (e.g., the apple) required more red in the background to be judged a match than did the objects that were not associated with the color red. This suggests that the knowledge of the objects was influencing people to perceive them as being more red than other objects (Figure 1.22). Hansen, Olkkonen, Walter, and Gegenfurtner (2006) replicated this basic finding. They presented participants with photographs of fruit such as bananas and simple patches of colors. Participants were asked to adjust the color of the object (banana or patch) to the uniform gray background. Hansen et al. found that participants adjusted the fruits differently than the patches of equivalent color. For example, participants added more blue to the banana in order to cancel out the more perceived yellowness of it (we will discuss color cancellation more in Chapter 6). Hansen and colleagues suggest that this implies that the cognitive association of objects to color influences how we perceive that color. |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

[고2] 2024년 10월 – 41~42번: 유전체 복제 과정에서 발생하는 돌연변이의 누적 원리 설명
In each round of genome copying in our body, there is still about a 70 percent chance that at least one pair of chromosomes will have an error. With each round of genome copying, errors accumulate. This is similar to alterations in medieval books. Each time a copy was made by hand, some changes were introduced accidentally; as changes stacked up, the copies may have acquired meanings at variance with the original. Similarly, genomes that have undergone more copying processes will have gathered more mistakes. To make things worse, mutations may damage genes responsible for error checking and repair of genomes, further accelerating the introduction of mutations. Most genome mutations do not have any noticeable effects. It is just like changing the i for a y in "kingdom" would not distort the word's readability. But sometimes a mutation to a human gene results in, for example, an eye whose iris is of two different colors. Similarly, almost everyone has birthmarks, which are due to mutations that occurred as our body's cells multiplied to form skin. If mutations are changes to the genome of one particular cell, how can a patch of cells in an iris or a whole patch of skin, consisting of many individual cells, be affected simultaneously? The answer lies in the cell lineage, the developmental history of a tissue from particular cells through to their fully differentiated state. If the mutation occurred early on in the lineage of the developing iris, then all cells in that patch have inherited that change.
문제와 원문 출처 (링크 바로가기 클릭)


원문 텍스트 및 OCR
  |
A full 1 percent of our genes are involved in proofreading and correcting chromosomes. But despite this substantial investment in error correction, DNA copying is not perfect. In each cell division, there are 6 billion letter pairs to copy, check, and correct. The chance for one specific DNA letter pair to be mutated in one such duplication round (the mutation rate) is about 1 in 10 billion. Thus, in each round of genome copying, there is still about a 70 percent chance that at least one pair of letters will have a typo. This number is optimistic, because it assumes that you lead a healthy life. Your genomes can suffer even more changes through toxic chemicals (such as those in cigarette smoke or burned meat) or exposure to ultraviolet radiation (from the sun or visits to tanning salons). Such mutations can be single letters exchanged for others, as in the example above, but in some cases, entire segments of the DNA molecule (whole stretches of letters) are removed or are duplicated and added at seemingly random places. Because of these mutations, you do not have one single genome, but instead many billions of slightly different genomes, one for each of your cells. With each round of genome copying, errors accumulate. This is analogous to alterations in medieval books, which were copied by hand. Each time a copy was made, some changes were introduced inadvertently; over time, as changes accumulated, the copies may have accrued meanings at variance with the original. Similarly, genomes that have undergone more copying processes will have accumulated more mistakes. To make things worse, mutations may damage those genes responsible for the proofreading and repair of genomes, further accelerating the introduction of mutations. Most mutations do not have any noticeable effects, just like changing the *i* for a *y* in “kingdom” would not distort the word’s legibility or meaning. But sometimes a mutation to a human gene results in, for example, an eye whose iris is of two different colors. Similarly, almost everyone has birthmarks, which are due to mutations that occurred as our body’s cells multiplied to form skin. But if mutations are changes to the genome of one particular cell, how can a patch of cells in an iris or a whole patch of skin, consisting of many individual cells, be affected simultaneously? Were all of the millions of cells in the iris of a girl with a blue patch in an otherwise brown eye struck by the same mutation? The answer lies in the cell lineage: if the mutation occurred early on in the lineage of the developing iris, then all cells in that patch have inherited that change. |
텍스트 비교 (문제 텍스트 vs. 원문 텍스트)

관련 자료 바로가기
[고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 지문 출처 (20~24번)
[고2] 2024년 10월 – 20번: 수학적 비판적 사고를 교육과 의사결정 과정에서 강조해야 함 To be mathematically literate means to be able to think critically about societal issues on which mathematics has bearing so as to
flowedu.tistory.com
[고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 지문 출처 (29~34번)
[고2] 2024년 10월 – 29번: 동물이 특정 경험을 선호하거나 회피하는지 확인하는 방법 Conditioned Place Preference is a way of finding out what animals want. Researchers train them to associate one place with an experienc
flowedu.tistory.com
'[고2] 영어 모의고사 자료 > [고2] 24년 10월 자료' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 영어지문요약 with images (by gemini-2.5-pro) (0) | 2025.12.03 |
|---|---|
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 지문 출처 (29~34번) (2) | 2024.11.23 |
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 지문 출처 (20~24번) (0) | 2024.11.23 |
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 지문 요약 by ChatGPT-4o (0) | 2024.10.21 |
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 한줄해석 (좌지문 우해석) (1) | 2024.10.19 |
| [고2] 2024년 10월 모의고사 - 한줄해석 (0) | 2024.10.19 |